Androgenic alopecia or male pattern baldness is the common type of hair loss that occurs in men. The exact reason for this type of hair loss is unknown, but it is believed that genetic, hormonal and environmental factors are all responsible for this. DHT is thought to be the major factor amongst all.
Some key points about DHT that you need to know are given below:
- DHT is an androgen hormone that helps in giving males their male characteristics.
- DHT is believed to cause hair follicles to miniaturize, which plays a major role in causing male pattern baldness.
- By the age of 50 years, over half of the men probably experience hair loss mediated by DHT.
- The treatments and medications that block DHT may help prevent hair loss and baldness.
So, the above-mentioned were the fast facts on DHT; now let’s study the different aspects of DHT in detail!
What is DHT?
DHT stands for Dihydrotestosterone and it is also known as an androgen hormone. It is a sex steroid produced in the gonads. This androgen hormone is responsible for the multiple biological characteristics of men such as body hair, increased muscle mass and a deeper voice.
The high levels of DHT can cause certain problems like hair loss while having too little DHT can also increase the risk for certain problems in your sexual development as you go through puberty.
Generally, the low levels of DHT do not have much effect on women, but in men, it can lead to several complex issues:
- Changes in body fat distribution
- Incomplete or late development of sex organs
- Risk of developing aggressive prostate tumors
More about DHT
DHT has many roles. Apart from hair production, it is linked to benign prostatic hyperplasia or an enlarged prostate. During fetal development, DHT plays a fundamental role in the development of the penis and prostate gland.
DHT is androgens or hormones that contribute to male sex characteristics when they go through puberty. These traits include:
- a deep voice
- increased body hair and muscle mass
- growth of the penis, scrotum, and testicles as sperm production begins
- changes in how fat is stored around your body
Why DHT affect people?
- Your tendency to hair loss is genetic, which means it is passed down in your family. Hair at the temples and on the crown slowly thin and eventually disappears.
- For example, if you are male and your father experiences male pattern balding, then it is likely that you’ll show an identical balding pattern as you age. If you are already inclined to male pattern baldness, the follicle-shrinking effect of DHT tends to be more pronounced.
- The size and shape of your head may also contribute to how quickly DHT shrinks your follicles.
How DHT Causes Hair Loss?
When the anagen phase of hair follicles is diminished and the telogen phase becomes longer, then the problem of male pattern baldness starts taking place. The anagen phase is the growth phase of hair and the shortened growth phase means that the hair follicles are not growing as long as they did before.
The telogen phase of the hair growth cycle is less well-anchored to the scalp, thus making it easier to fall out. With each cycle of growth, the hair shaft becomes thinner as the follicles become smaller. Eventually, hairs are reduced to vellus follicles; the type of soft, light hairs that cover an infant and mostly disappear in response to androgens.
Three Phases of Hair Growth Cycle
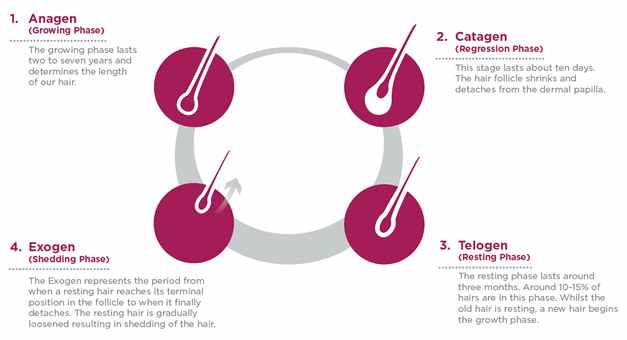
- Anagen Phase: It is the initial phase that is also known as the growth phase. The hair follicles remain in this phase for around 2 to 6 years. The longer it lasts, the longer the hair grows. In general, approximately 80 to 85 percent of the hair strands on the head are in the anagen phase.
- Catagen Phase: It is the middle phase that lasts only for 10 – 14 days. This phase allows the hair follicle to renew itself.
- Telogen Phase: It is the final, resting state of the hair follicle where it lies dormant for 1 to 4 months. Usually, between 12 – 20 percent of hairs are in the resting phase
- Exogen PHase: It Represents the period from when a resting hair reaches its terminal position in the follicle from when it can finally detach. The rest of the hairs are usually loosened resulting in shedding of the hair.
How to Control DHT?
A number of medications for DHT related hair loss are available. Some of them are proven medications that target DHT production specifically.
The best way to control and block DHT production is to use finasteride along with minoxidil and shampoo that can help in blocking DHT in your scalp.
Is there any side effect of blocking DHT?
For most of the men, blocking DHT does not result in any noticeable or major side effects. Generally, the people who take medications like finasteride and topical DHT blockers do not experience any negative effects. But there are some rare cases as well, where men have to suffer from some potential downsides such as lower sex drive, higher testosterone, and weak erections. If you are facing these side effects, then you can reduce the amount of taking finasteride.
Finasteride & DHT
What’s the connection between these two terms?
Well! Finasteride is a drug medication that is used to reduce the levels of DHT in the scalp. It is an oral medication that helps keep DHT from binding to receptors on your hair follicles and protects them from shedding away. A daily dose of approximately 1mg of finasteride helps in blocking the production of DHT to stop hair loss. In some cases, it can even help the damaged follicles to start to grow back.
The earlier you start blocking DHT, the more successfully you can prevent hair loss. This is because once the hair is gone; no amount of DHT blockers can bring your hair back!




 can help you
can help you





